
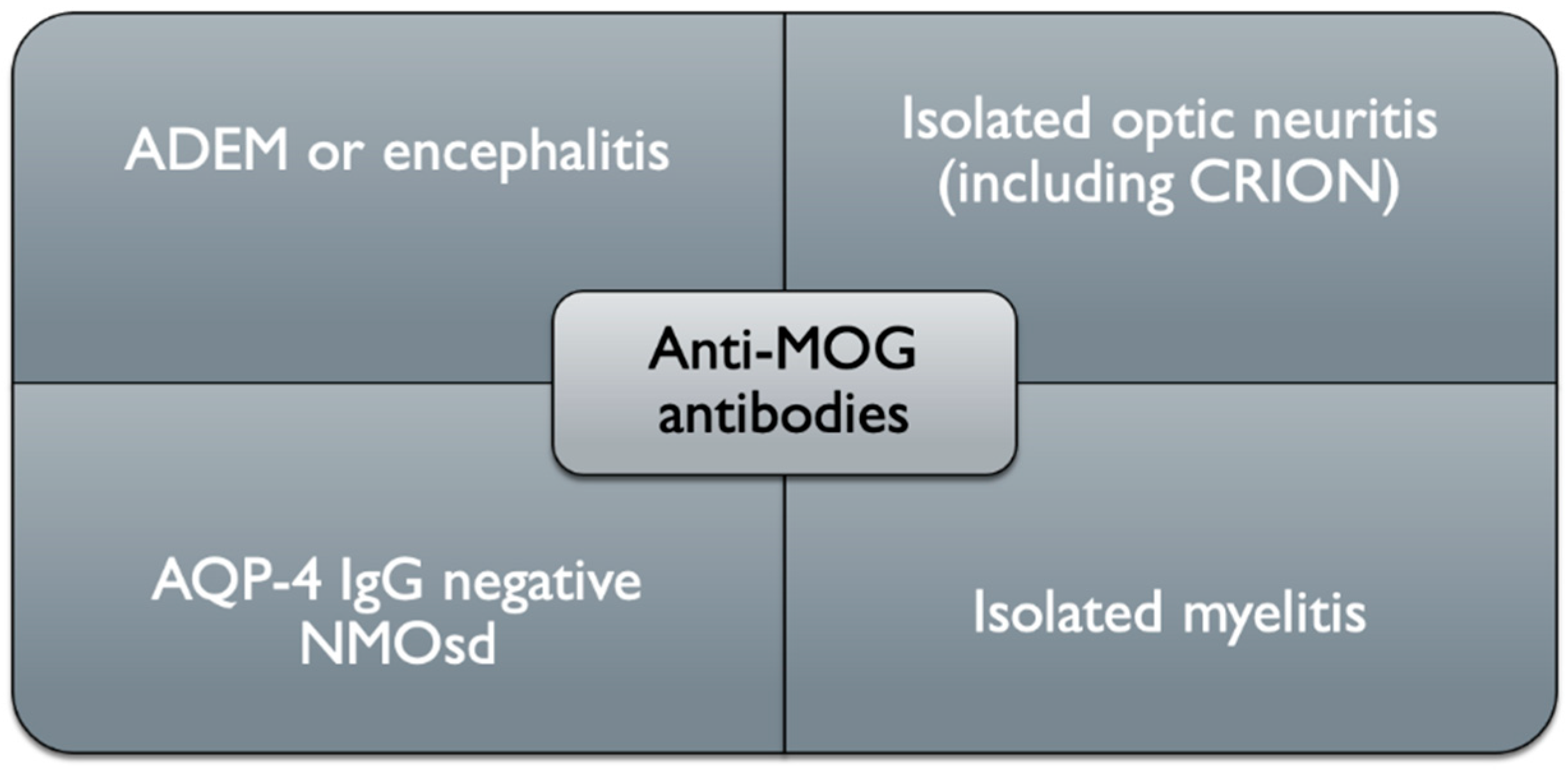
Even though these conditions are fundamentally similar, research into genetic factors, their unique clinical manifestations, and lesion pathology has helped with differential diagnosis and disease pathogenesis knowledge. Each disease is caused by a complex combination of genetic and environmental variables, many involving an autoimmune response. The grouping of human central nervous system demyelinating disorders today includes multiple sclerosis (MS) and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD) as distinct disease categories.

We present a case of an elderly man who presented with fever, fits, hyponatremia, and polyuria following COVID-19 vaccination and was found to have cerebral salt wasting (CSW) with the exclusion of other causes.ĭemyelinating diseases alter myelin or the coating surrounding most nerve fibers in the central and peripheral nervous systems. There are some reported neurological complications, such as ischemic stroke, Guillain-Barré syndrome, transverse myelitis, Bell's palsy, cerebral venous sinus thrombosis, optic neuritis, meningoencephalitis, small fiber neuropathy, and Tolosa-Hunt syndrome. There are many neurological complications reported by SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. Currently, more than 10 vaccines are available against SARS-CoV-2 infection globally. As any vaccine can have some side effects, COVID-19 vaccines also need surveillance and reporting side effects worldwide.

During this challenging time, vaccine production has been hugely carried out leading to the invention of many vaccines against COVID-19. Abbreviations: DCP = deep capillary plexus EDSS = Expanded Disability Status Scale GCC = ganglion cell complex GCL = ganglion cell layer MRI = magnetic resonance imaging MS = Multiple sclerosis OCT = optical coherence tomography OCT-A = optical coherence tomography angiography ON = optic neuritis RNFL = retinal nerve fiber layer SCP = superficial capillary plexus VD = vessel density.Ĭoronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) pandemic caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) occurred worldwide, and it affected millions of people around the world and killed millions of lives without a definitive treatment. Conclusions: OCT and OCT-A parameters could improve the development of retinal biomarkers for screening, early diagnosis and monitoring the disease progression of MS, and they could improve the development of potential future therapies that could slow or stop the course of this incurable disease. The reduced retinal vessel density (VD) was correlated with the disability in MS. Retinal capillary plexuses could be higher, lower or the same, and the best OCT-A microvasculature parameter for the detection of MS was the superficial capillary plexus (SCP). Results: Retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) and ganglion cell layer (GCL) were significantly lower in MS patients compared to controls, and correlated with clinical and paraclinical variables, such as visual function, disability, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Additional studies were found via references, being chosen according to relevance. Methods: To carry out this review, a meticulous literature search was undergone on PubMed between 2014 and the present day, using the following terms: "multiple", "sclerosis", "optical", "coherence", "tomography" and "angiography". The aim of this review was to highlight the most current optical coherence tomography (OCT) and optical coherence tomography angiography (OCT-A) data in MS and to provide information about the possibility of using OCT / OCT-A parameters as biomarkers for screening, diagnosis and monitoring of MS.

Objective: Retinal neuronal and vascular changes have been observed in multiple sclerosis (MS) patients.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
